Model Entities
Overview
The Model entities section of ROI iAM provides an overview of all predefined model entities, and gives the tools to create new ones, modify or delete them.
Model entities are fundamental components in ROI iAM which enable the encapsulation of Attribute Schemas and Events with respective handler processes, and form a unified Entity representation.
There are two views available: list and details view. The list view displays all available model entities, while the details view allows you to view and edit the details of a selected interface.
Access
To learn more about the necessary access and prerequisite requirements for this section, please review the following documentation: Security
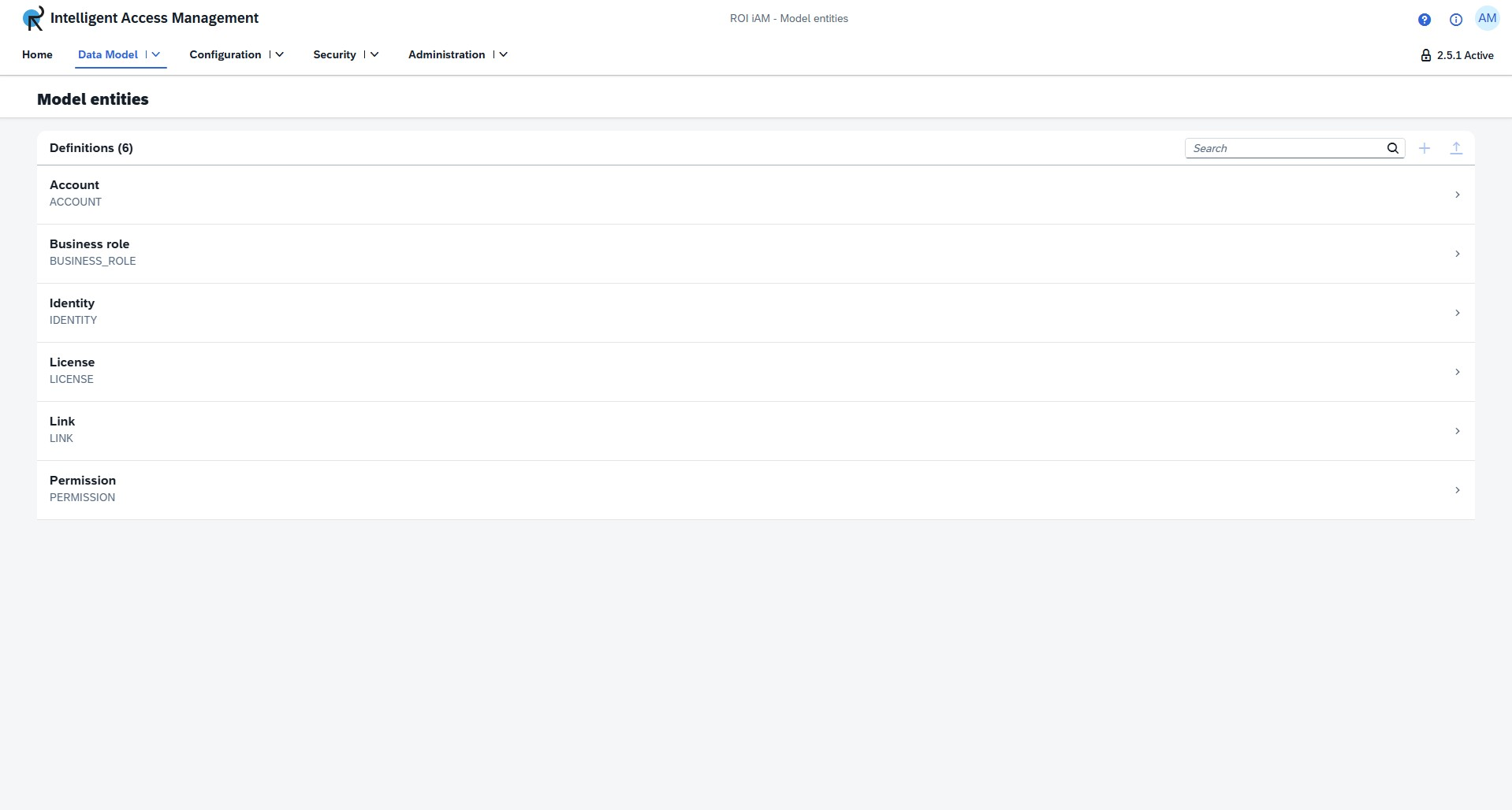
List view
The list view displays all model entities in the current version or revision. Model entities can be custom or built-in. Custom entities appear with a blue custom tag.
Creating a model entity
To create a new model entity:
- Press the Create button, located next to the search bar.
- Input a Display Name. - This field is mandatory. This will always become the technical name of the model entity.
- Input a Description. - This field is mandatory and can contain up to 512 characters.
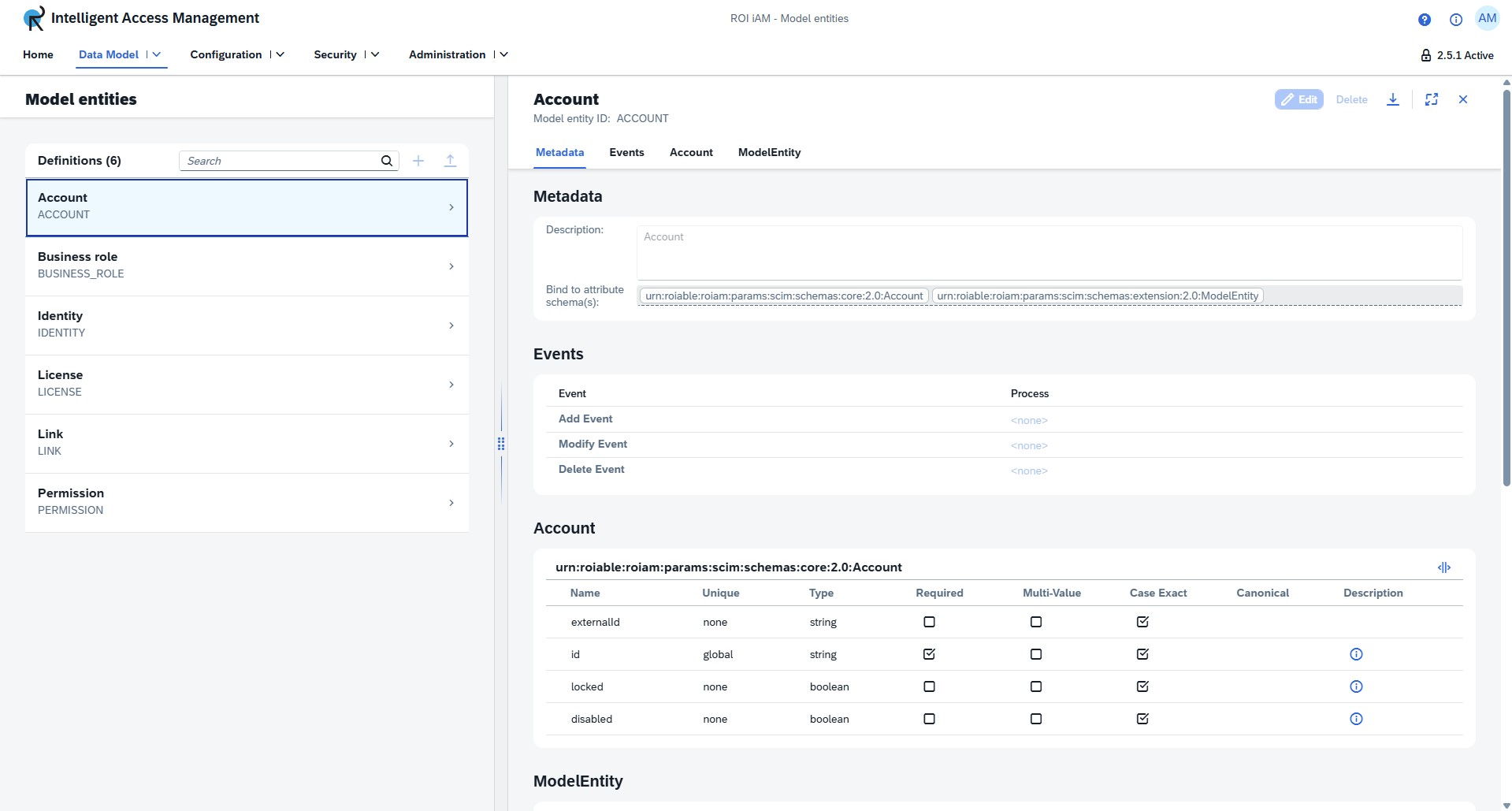
Details view
The details view provides an overview of the bound attribute schemas and events. These can be edited when on a non-active version or revision.
The controls for the details view are located in the upper right corner. Left to right, we have the following buttons:
- Edit - Enters edit mode, allowing you to modify the model entity details.
- Delete - Deletes the model entity.
INFO
Only Custom entities can be deleted.
- Export - Exports the model entity.
Edit mode
Metadata
Model entities include essential metadata fields that define their properties and integration points within the ROI iAM system.
Description - A text field that provides a clear explanation of what the model entity represents and its purpose within the IAM system. This helps administrators and developers understand the entity's role and use case.
Bind to Attribute Schema - Links the model entity to a specific attribute schema that defines its structure and available attributes. The schema binding uses the URN (Uniform Resource Name) format to ensure globally unique identification.
Example:
urn:roiable:roiam:params:scim:schemas:extension:2.0:ModelEntityEvents
Model entities can trigger automated processes in response to lifecycle events. Each event type can be configured to execute specific workflows when data changes occur.
Event Types
| Event | Process | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Add Event | <none> | Triggered when a new instance of the model entity is created. Can be configured to initiate onboarding workflows or provisioning processes. |
| Modify Event | <none> | Triggered when an existing model entity instance is updated. Can be used to propagate changes during update workflows. |
| Delete Event | <none> | Triggered when a model entity instance is removed. Can be configured to handle deprovisioning or cleanup operations. |
Note: By default, events are set to <none>, meaning no automated process is triggered. Administrators can configure specific processes to execute for each event type based on business requirements.